The following command will show what network traffic is in use at the port level:
Netstat -a -n -oThe -o parameter will display the associated process identifier (PID) using the port. This command will produce an output similar to what is in Figure A.
Figure A
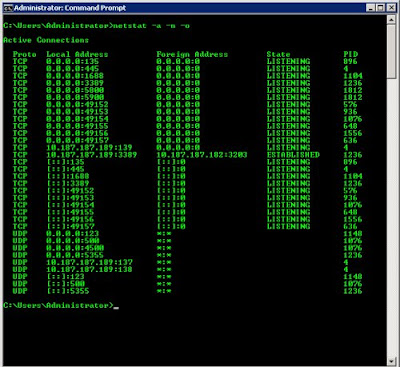
With the PIDs listed in the netstat output, you can follow up with the Windows Task Manager (taskmgr.exe) or run a script with a specific PID that is using a port from the previous step. You can then use the tasklist command with the specific PID that corresponds to a port in question. From the previous example, ports 5800 and 5900 are used by PID 1812, so using the tasklist command will show you the process using the ports. Figure B shows this query.
Figure B
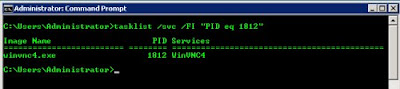
This identifies VNC as the culprit to using the port. While a quick Google search on ports could possibly obtain the same result, this procedure can be extremely helpful when you’re trying to identify a viral process that may be running on the Windows Server.
No comments:
Post a Comment